Project Summary: The Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO) of the UK government has invested in the ‘Strengthening Midwifery in Bangladesh’ program to establish midwifery education. The FCDO is also providing technical assistance to the Government of Bangladesh through UNFPA. The government has demonstrated commitment to midwifery services by creating 2996 midwife posts. Currently, there are
- Published in Maternal Newborn Child and Reproductive Health, Our Work
No Comments
Creating responsive health systems: improving the use of feedback from service users in quality assurance and human resource management in Bangladesh. is a project that aims to assist policymakers in designing a comprehensive health-systems intervention to make Bangladesh’s health system more responsive. It will do so through assessing the current system of collecting, and
- Published in Health Systems, Our Work
The main objective of this World Health Organization (WHO) funded project was to identify the barriers and facilitators of physical activities to reach Global Action Plan on the prevention of NCDs in Bangladesh. The situation analysis also attempted to provide an overall view of the current scenario regarding the presence of physical activity as a
- Published in Health Systems, Our Work
Muslim Communities Learning About Second-hand Smoke (MCLASS-II) in Bangladesh is an effectiveness-implementation hybrid study funded by the Medical Research Council, UK. Its overall aim is to reduce the burden of disease due to second-hand smoke in low- and middle-income countries by discovering innovative community-based approaches to behaviour change. It will assess the feasibility and
- Published in Health Systems, Our Work
Intervention for Mothers in Pregnancy to Reduce Exposure to Secondhand Smoking (IMPRESS) is a study that aimed to culturally adapt, and then evaluate, the effectiveness of evidence-based strategies to reduce second-hand smoking within homes in the peri-urban area of Bangladesh. It also aimed to determine the costs versus benefits of implementing such an intervention.A
- Published in Maternal Newborn Child and Reproductive Health, Our Work
The overall long-term aim of this research programme is to improve health outcomes and quality of life for people with depression and tuberculosis in South Asia. This study is aimed carring out the preliminary work for a future trial to evaluate depression care integrated with tuberculosis services. The specific objectives are: To understand the
- Published in Non-Communicable Disease, Our Work
This project aimed to develop and evaluate a service delivery model for the delivery of quality care to patients of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and diabetes at the Upazila Health Complexes and other primary health care (PHC) facilities. Specific objectives included: establishing a systematic screening and care process to enhance early diagnosis of CVD and
- Published in Non-Communicable Disease, Our Work
Improving primary health care using community clinics in rural Bangladesh is a project that aimed to improve the quality of care of children in community clinics through an intervention and evaluation study. The intervention contributed to a change in national policy and practice, with approximately 14,000 community health care providers nationwide given the job
- Published in Health Systems, Our Work
Abstract Introduction The burden of multimorbidity is recognised increasingly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), creating a strong emphasis on the need for effective evidence-based interventions. Core outcome sets (COS) appropriate for the study of multimorbidity in LMICs do not presently exist. These are required to standardise reporting and contribute to a consistent and cohesive
- Published in Journal Article, Resources
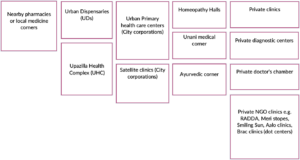
By Umme Salma Anee, Masroor Salauddin, Sadika Afrin, Faiaz Chowdhury, Nabila Binth Jahan, Deepa Barua, Rumana Huque, Helen Elsey Urban regions in Bangladesh are now more densely populated as a result of migration and industrialization. With a population rise of 3.26% from 2022 to 2023, Dhaka, the country’s largest metropolis that is growing day by
- Published in Blog